Circular economy: recovering to create value
What is the circular economy?
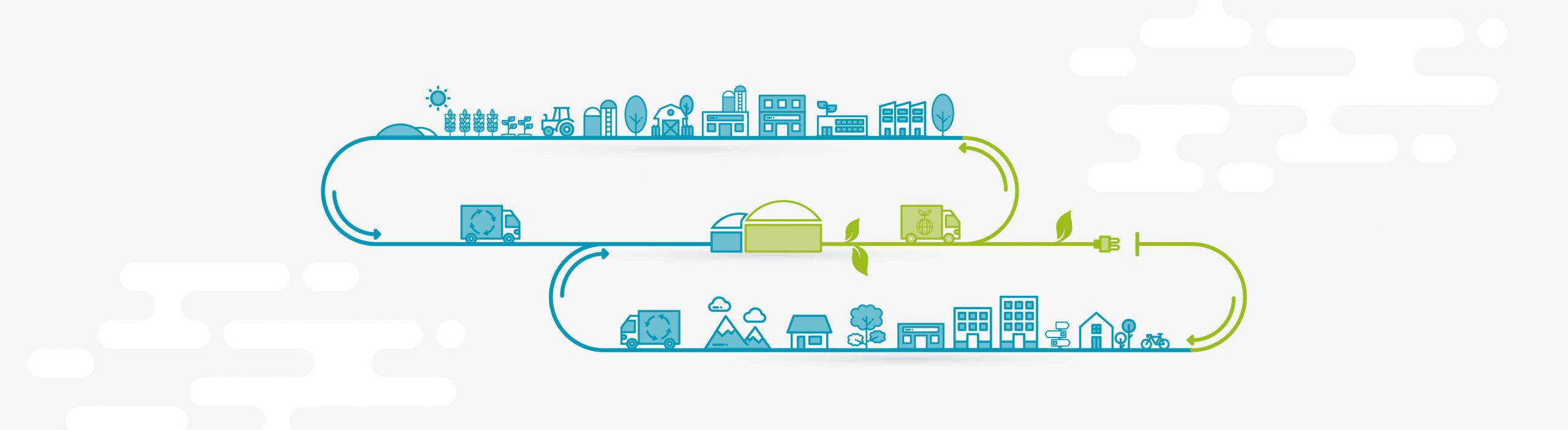
The circular economy is a model based on the idea of an economy that is capable of regenerating itself.
The term circular is used precisely to indicate the contrast with the common (linear) economic model based on: production, use and waste.

 Return biological materials to the environment
Return biological materials to the environment Give new life to technological components, preventing them from affecting the environment
Give new life to technological components, preventing them from affecting the environmentIn fact, in the case of the circular economy the key concept is the recovery and reuse of existing materials and products.
Once it reaches the end of its life cycle, a product can be broken down into its parts and reintroduced into the economic cycle, thereby reusing it in the production cycle and generating value.

The benefits of the circular economy
Unlike the linear economic model which provides for enormous quantities of energy and raw materials to be used in the production phase and which does not focus on the problem of waste, the circular economy starts from waste, to reduce the quantities and lengthen the life-cycle of products.
The circular economy results in:
A favorable impact on the climate. Reduction of energy consumption and CO₂ emissions

More rational use and processing of raw materials, to reduce environmental exploitation

Increased competitiveness and a drive towards innovation

Economic and employment growth
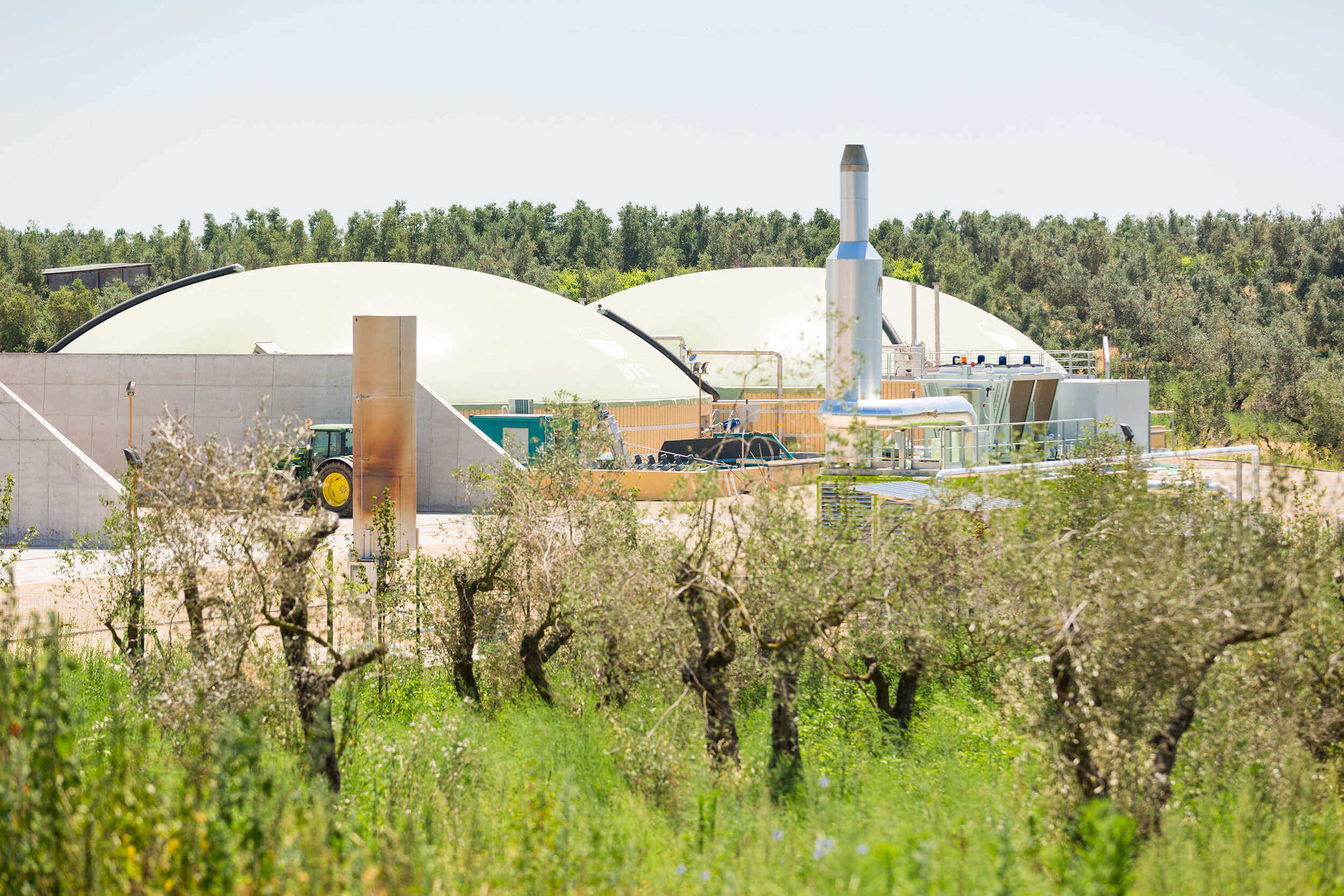

Where it is not possible to avoid the production of waste, its economic value must be recovered, minimizing the impact on the environment, in line with the European Union strategy and the Paris agreement of 2015, but above all for the environmental benefits. in terms of lower CO2 emissions.
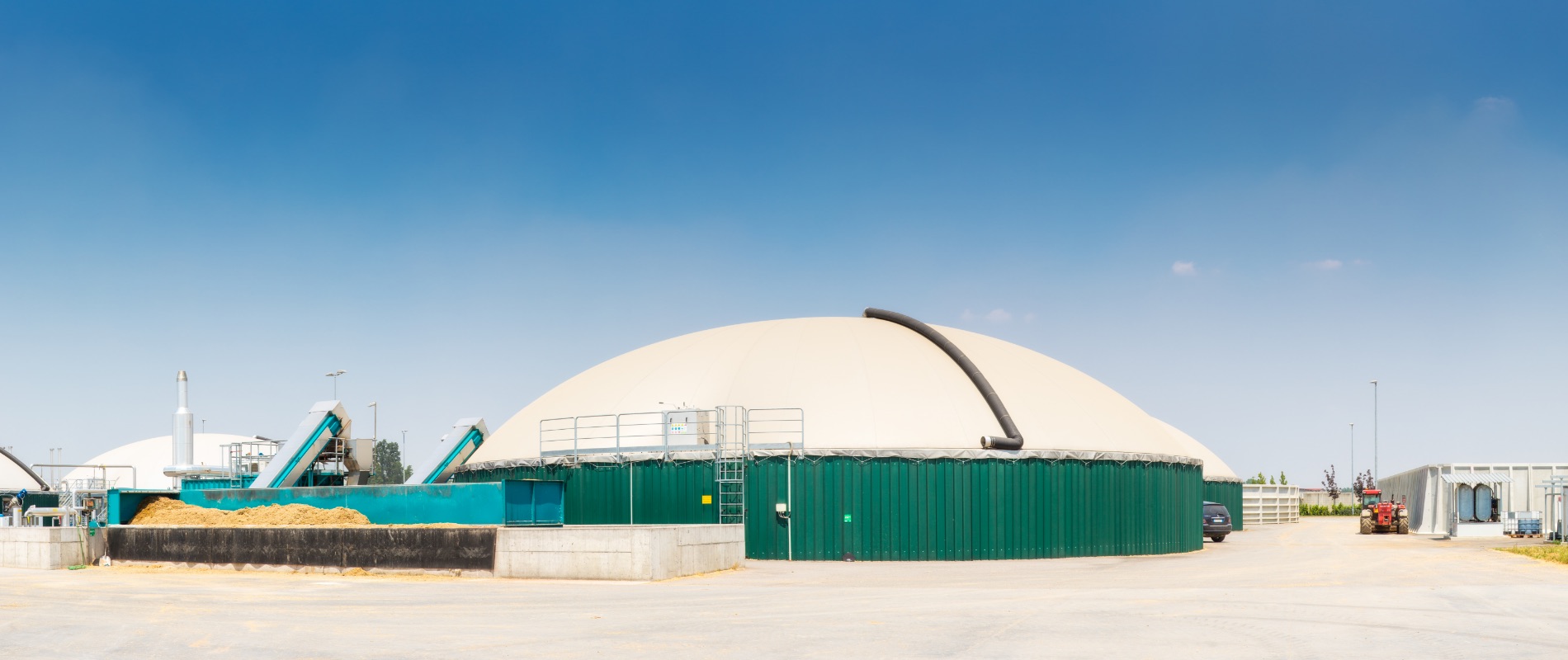
Waste management
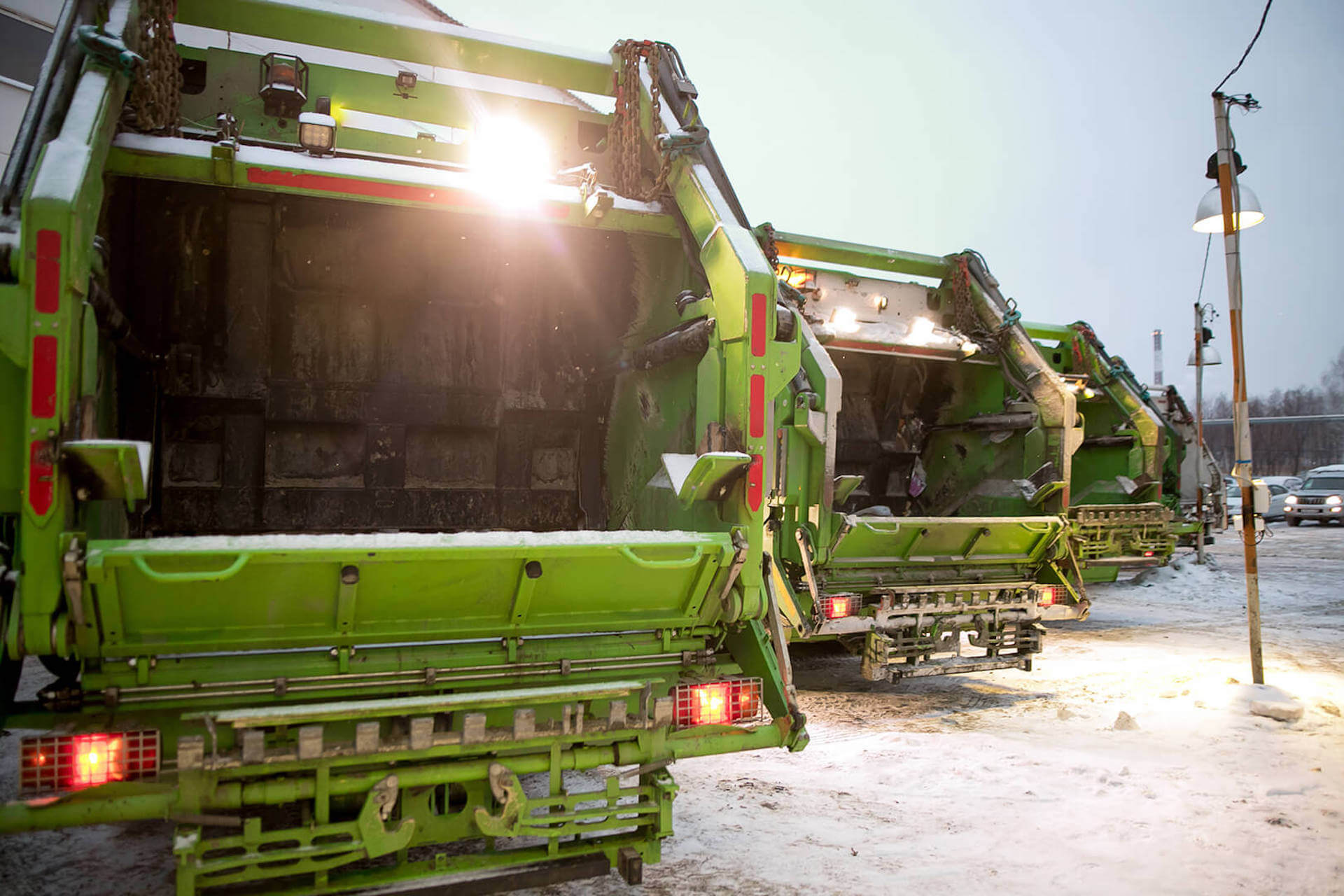

The evolution towards the circular economy is now an unstoppable process and passes through the recycling of by-products and waste generated by our cities, agro-industries and agriculture, to become a precious resource for the production of renewable energy.
Agricultural plants
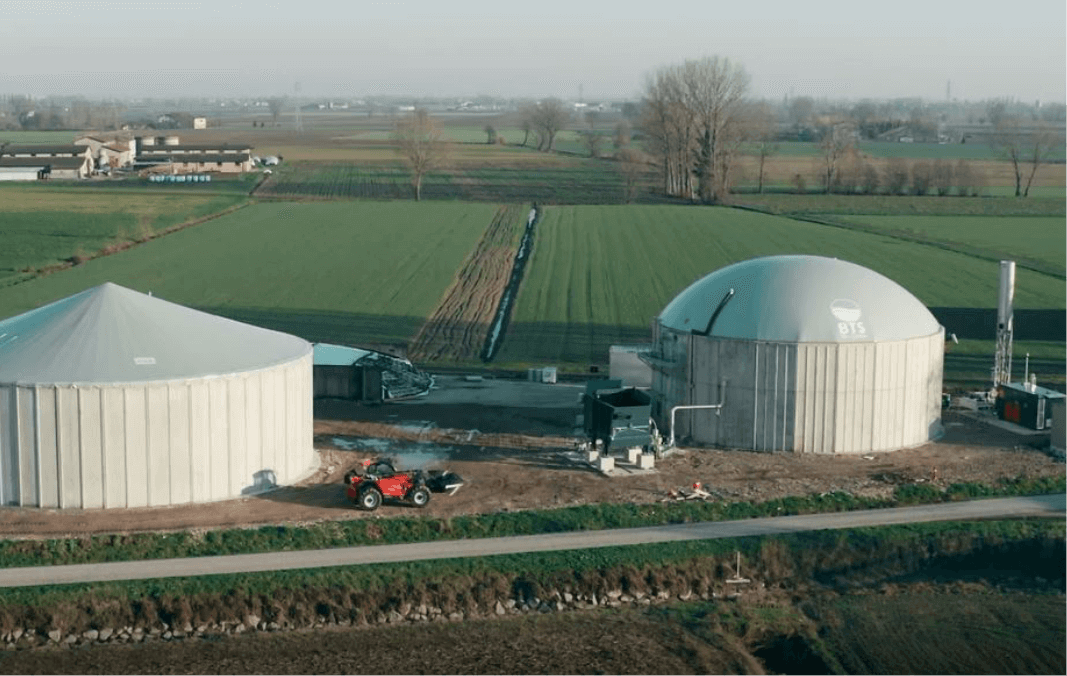

A great opportunity to revisit and enhance the processes aimed at better resource efficiency, focusing on a more sustainable and environmentally friendly economic activity that creates income and employment.
Agro-industrial plants
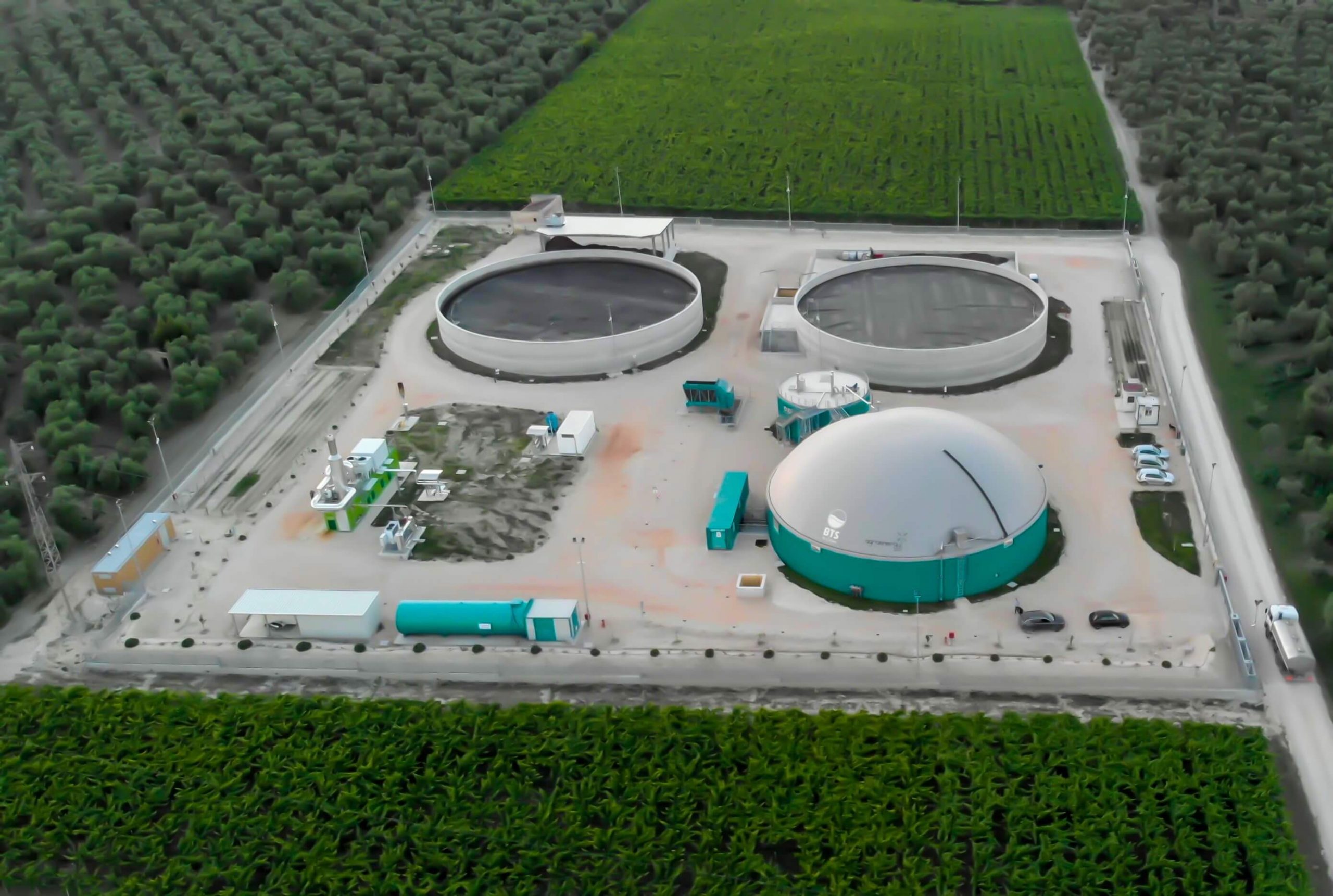

Where it is not possible to avoid the production of waste, its economic value must be recovered, minimizing the impact on the environment, in line with the European Union strategy and the Paris agreement of 2015, but above all for the environmental benefits. in terms of lower CO2 emissions.
Organic Waste