Biogas: renewable energy from residual materials
What is Biogas?
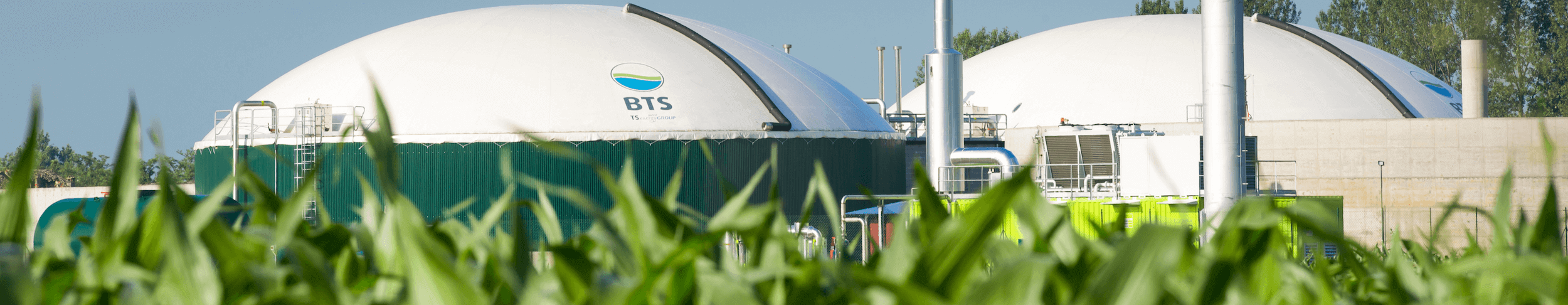
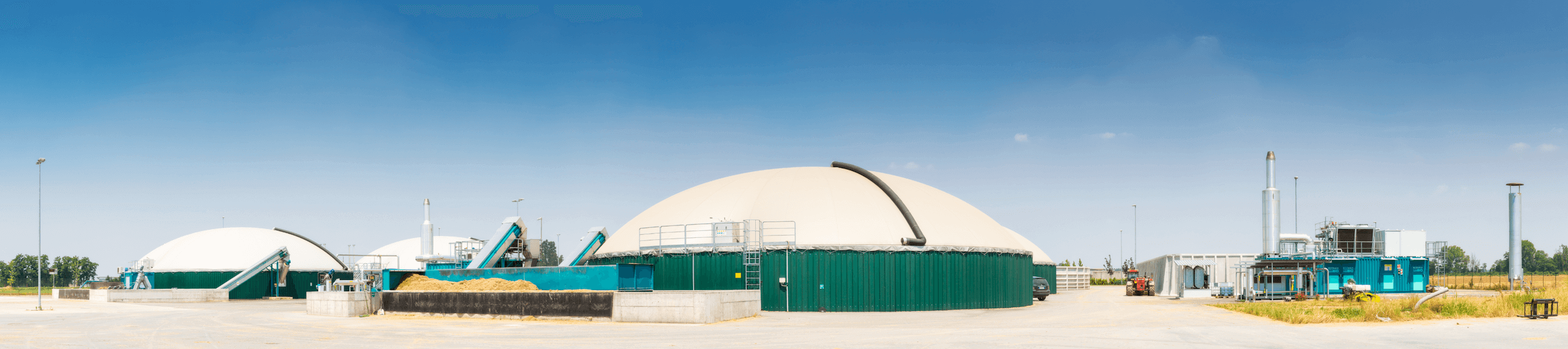
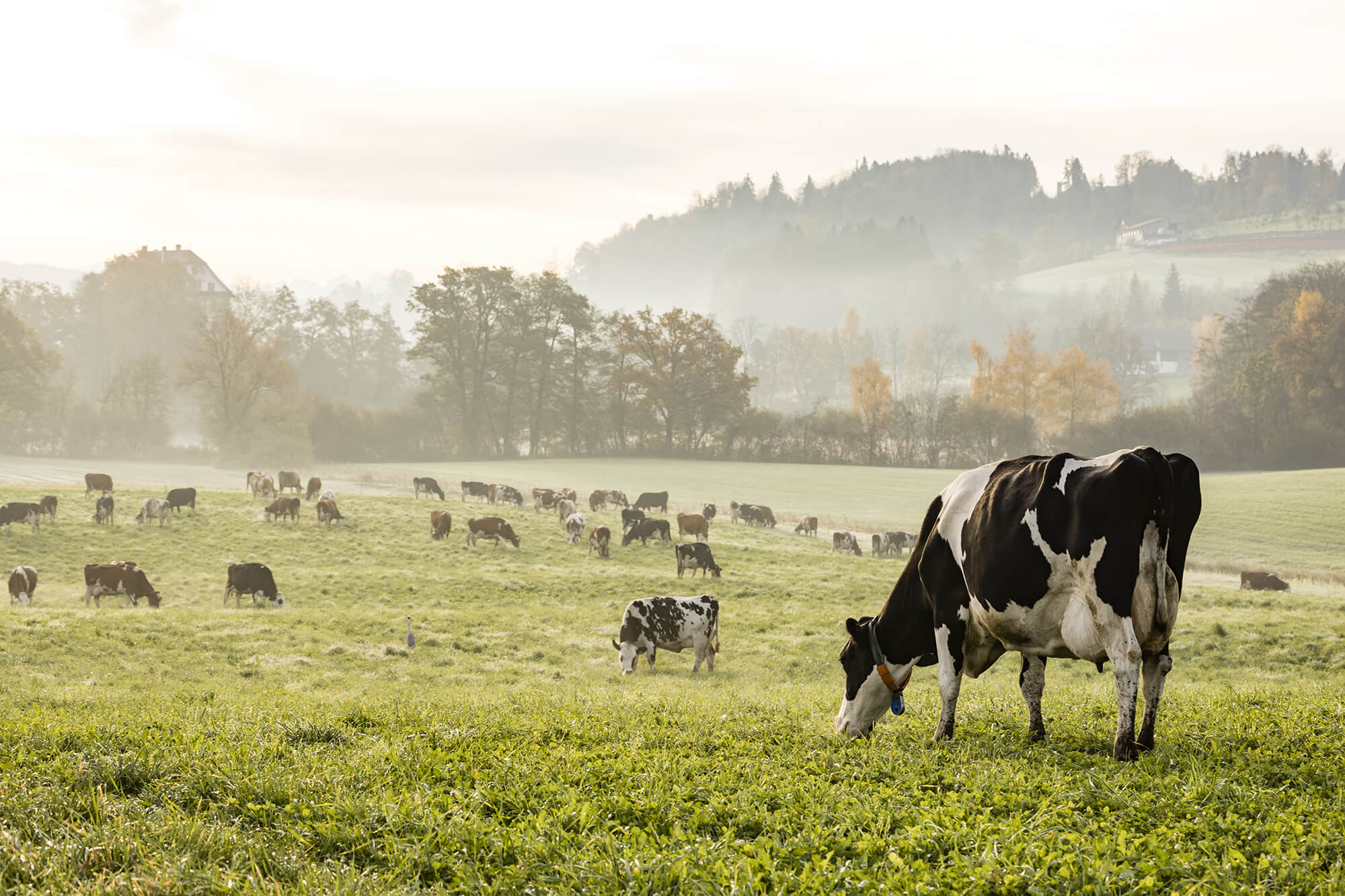
Biogas is a natural gaseous fuel.
It is obtained through anaerobic digestion, as a product of the fermentation of substances of organic origin, both animal and vegetable, by bacteria that live in the absence of oxygen, inside specific digesters.





What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a biochemical process which, in the absence of oxygen, leads to the degradation of complex organic substances with the production of biogas and digestate.
The process is carried out by different bacterial strains, each of which has a well-defined role and works to create a product that acts as a substrate for the action of the next bacterial strain.
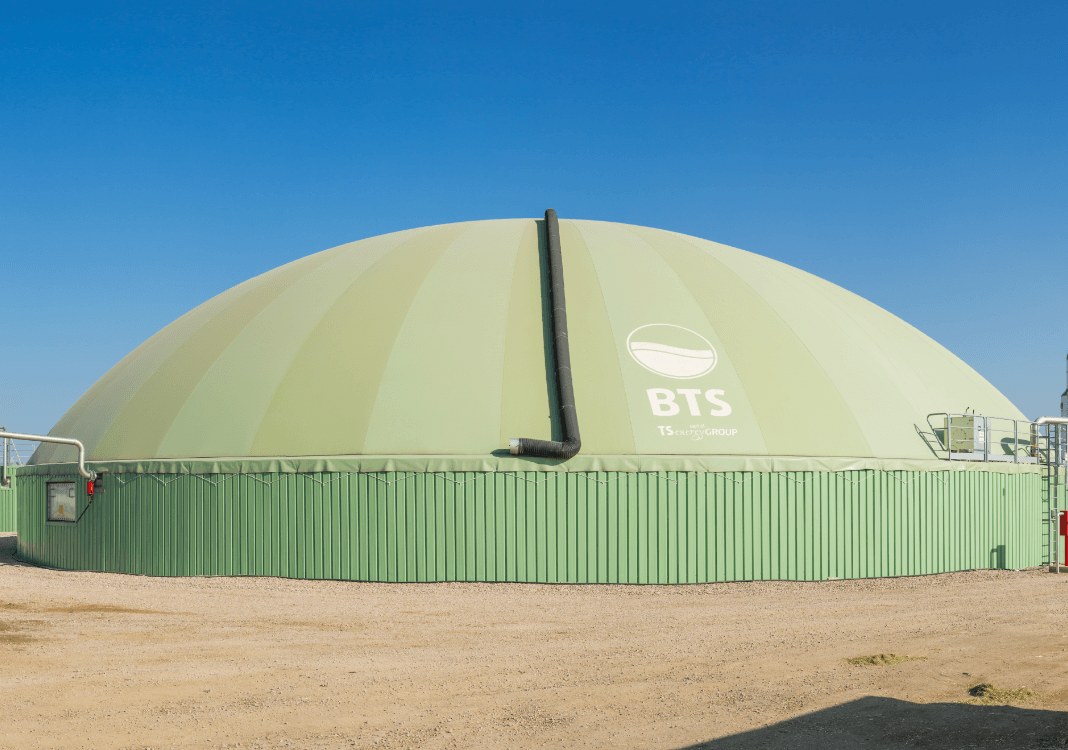

From anaerobic digestion to Biogas



The fermentation process is carried out by different bacterial strains that live in a mixed cultivation inside the fermenter at a temperature between 38 °C and 55 °C and with a pH of around 7-7.5.
There is a close correlation between the digestion temperature and the residence time in the fermenter. The optimal residence time is 40-60 days, but with temperatures above 45 °C it can be reduced to 25 days.